Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
Convert camera images to pixels on a s square grid#
7 import astropy.units as u
8 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
9
10 from ctapipe.image.toymodel import Gaussian
11 from ctapipe.instrument import SubarrayDescription
12 from ctapipe.visualization import CameraDisplay
get the subarray from an example file
16 subarray = SubarrayDescription.read("dataset://gamma_prod5.simtel.zst")
Geometries with square pixels#
Define a camera geometry and generate a dummy image:
37 CameraDisplay(geom, image)
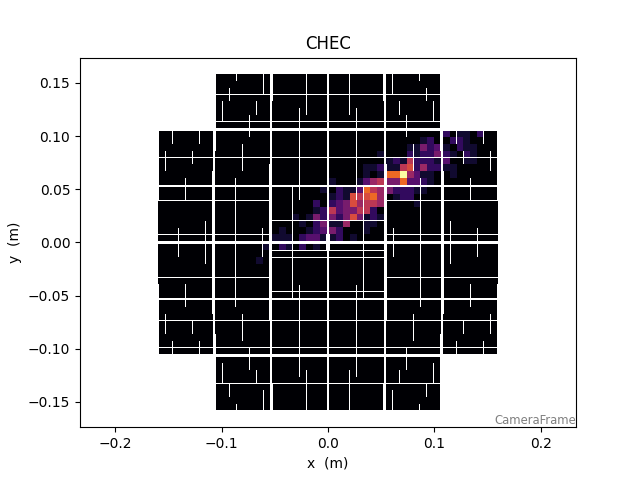
<ctapipe.visualization.mpl_camera.CameraDisplay object at 0x79f094d37c70>
The CameraGeometry has functions to convert the 1d image arrays to
2d arrays and back to the 1d array:
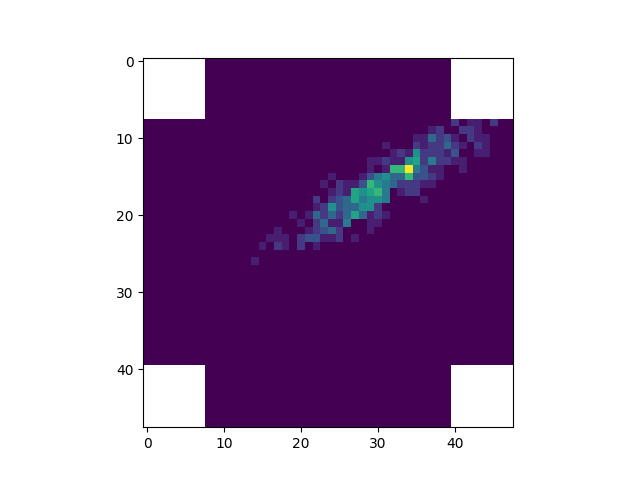
<matplotlib.image.AxesImage object at 0x79f08bac9a80>
54 CameraDisplay(geom, image_1d)
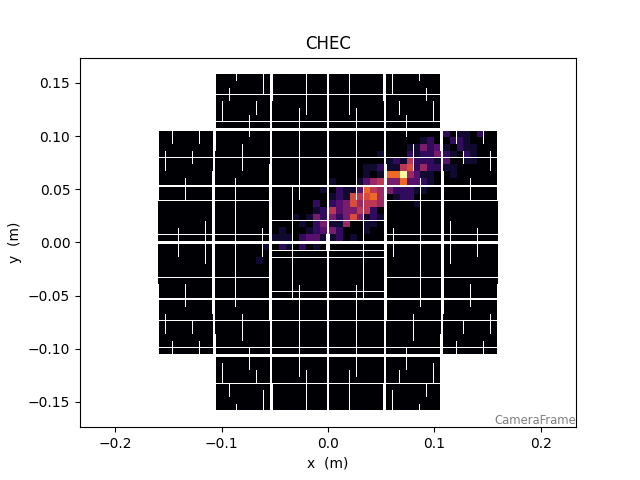
<ctapipe.visualization.mpl_camera.CameraDisplay object at 0x79f08af8a980>
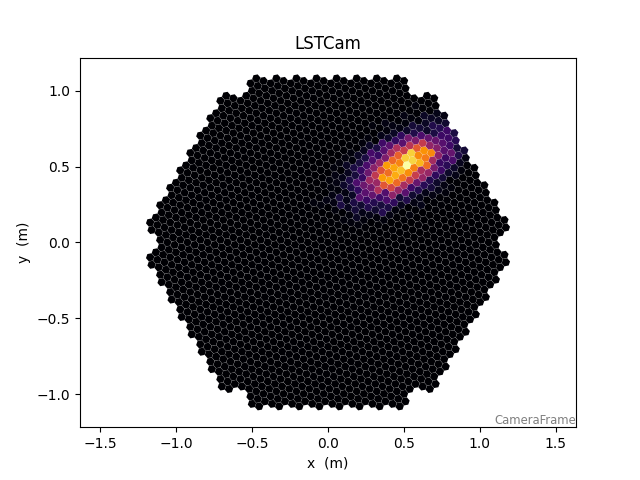
Geometries with hexagonal pixels#
Define a camera geometry and generate a dummy image:
75 CameraDisplay(geom, image)
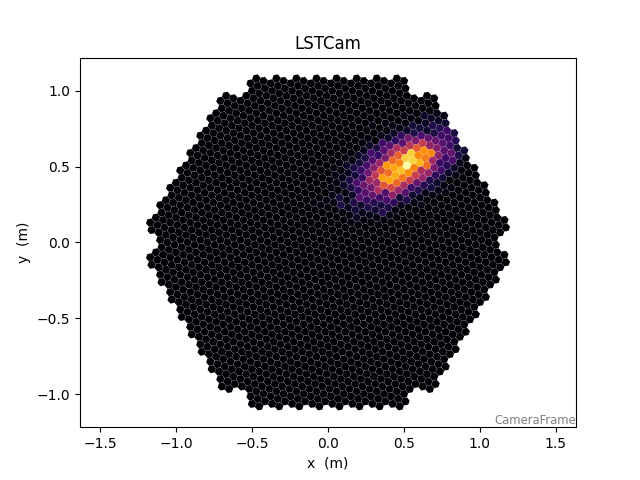
<ctapipe.visualization.mpl_camera.CameraDisplay object at 0x79f08b5d2800>
Conversion into square geometry#
Since the resulting array has square pixels, the pixel grid has to be
rotated and distorted. This is reversible (The
image_from_cartesian_representation method takes care of this):
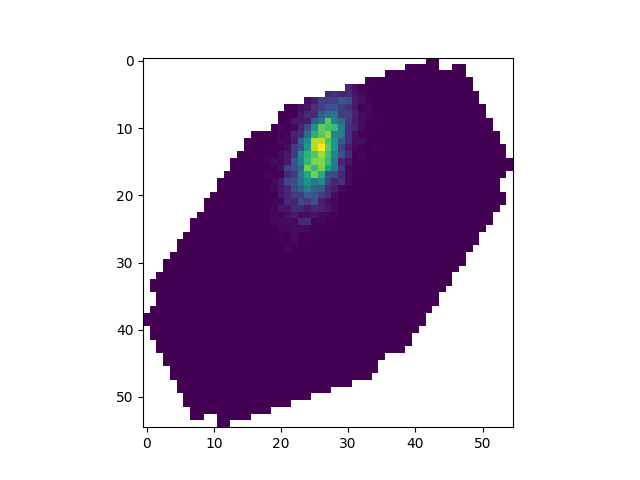
<matplotlib.image.AxesImage object at 0x79f08a954220>
96 disp = CameraDisplay(geom, image_1d)
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 1.693 seconds)

