Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
Getting Started with ctapipe#
This hands-on was presented at the Paris CTAO Consoritum meeting (K. Kosack)
Part 1: load and loop over data#
16 import glob
17
18 import numpy as np
19 import pandas as pd
20 from ipywidgets import interact
21 from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
22
23 from ctapipe import utils
24 from ctapipe.calib import CameraCalibrator
25 from ctapipe.image import hillas_parameters, tailcuts_clean
26 from ctapipe.io import EventSource, HDF5TableWriter
27 from ctapipe.visualization import CameraDisplay
28
29 # %matplotlib inline
32 path = utils.get_dataset_path("gamma_prod5.simtel.zst")
35 source = EventSource(path, max_events=5)
36
37 for event in source:
38 print(event.count, event.index.event_id, event.simulation.shower.energy)
0 4009 0.07287972420454025 TeV
1 5101 1.7454713582992554 TeV
2 5103 1.7454713582992554 TeV
3 5104 1.7454713582992554 TeV
4 5105 1.7454713582992554 TeV
41 event
ctapipe.containers.ArrayEventContainer:
index.*: event indexing information with default None
r0.*: Raw Data with default None
r1.*: R1 Calibrated Data with default None
dl0.*: DL0 Data Volume Reduced Data with default None
dl1.*: DL1 Calibrated image with default None
dl2.*: DL2 reconstruction info with default None
simulation.*: Simulated Event Information with default None
with type <class
'ctapipe.containers.SimulatedEventContainer'>
trigger.*: central trigger information with default None
count: number of events processed with default 0
monitoring.*: container for event-wise monitoring data (MON)
with default None
muon.*: Container for muon analysis results with default
None
44 event.r1
ctapipe.containers.R1Container:
tel[*]: map of tel_id to R1CameraContainer with default
None
47 for event in EventSource(path, max_events=5):
48 print(event.count, event.r1.tel.keys())
0 dict_keys([9, 14, 104])
1 dict_keys([26, 27, 29, 47, 53, 59, 69, 73, 121, 122, 124, 148, 162, 166])
2 dict_keys([82, 92, 175, 179])
3 dict_keys([17, 26, 27, 29, 43, 47, 53, 57, 69, 112, 121, 122, 124, 125, 128, 140, 144, 148, 162, 166])
4 dict_keys([3, 4, 8, 9, 14, 15, 23, 24, 25, 29, 32, 36, 42, 46, 52, 56, 103, 104, 109, 110, 118, 119, 120, 126, 127, 129, 130, 137, 139, 143, 161])
51 event.r0.tel[3]
ctapipe.containers.R0CameraContainer:
waveform: numpy array containing ADC samples: (n_channels,
n_pixels, n_samples) with default None
54 r0tel = event.r0.tel[3]
array([[[432, 413, 395, ..., 382, 387, 382],
[419, 420, 428, ..., 392, 396, 405],
[381, 392, 413, ..., 375, 387, 387],
...,
[391, 384, 385, ..., 379, 395, 404],
[370, 376, 388, ..., 391, 383, 383],
[393, 411, 413, ..., 406, 392, 396]],
[[413, 396, 398, ..., 397, 401, 395],
[392, 407, 403, ..., 403, 388, 399],
[405, 403, 393, ..., 393, 400, 409],
...,
[399, 406, 407, ..., 391, 405, 397],
[401, 399, 396, ..., 395, 400, 388],
[399, 393, 403, ..., 395, 407, 401]]],
shape=(2, 1855, 40), dtype=uint16)
(2, 1855, 40)
note that this is (\(N_{channels}\), \(N_{pixels}\), \(N_{samples}\))
68 plt.pcolormesh(r0tel.waveform[0])

<matplotlib.collections.QuadMesh object at 0x79f092887190>
71 brightest_pixel = np.argmax(r0tel.waveform[0].sum(axis=1))
72 print(f"pixel {brightest_pixel} has sum {r0tel.waveform[0,1535].sum()}")
pixel 1831 has sum 15824
75 plt.plot(r0tel.waveform[0, brightest_pixel], label="channel 0 (high-gain)")
76 plt.plot(r0tel.waveform[1, brightest_pixel], label="channel 1 (low-gain)")
77 plt.legend()
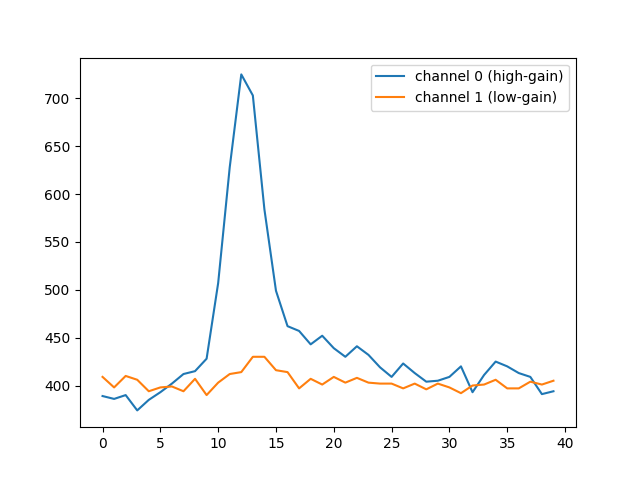
<matplotlib.legend.Legend object at 0x79f094b006a0>
81 @interact
82 def view_waveform(chan=0, pix_id=brightest_pixel):
83 plt.plot(r0tel.waveform[chan, pix_id])

interactive(children=(IntSlider(value=0, description='chan', max=1), IntSlider(value=1831, description='pix_id', max=5493, min=-1831), Output()), _dom_classes=('widget-interact',))
try making this compare 2 waveforms
Part 2: Explore the instrument description#
This is all well and good, but we don’t really know what camera or telescope this is… how do we get instrumental description info?
Currently this is returned inside the event (it will soon change to be separate in next version or so)
102 subarray = source.subarray
105 subarray
SubarrayDescription(name='MonteCarloArray', n_tels=180)
108 subarray.peek()
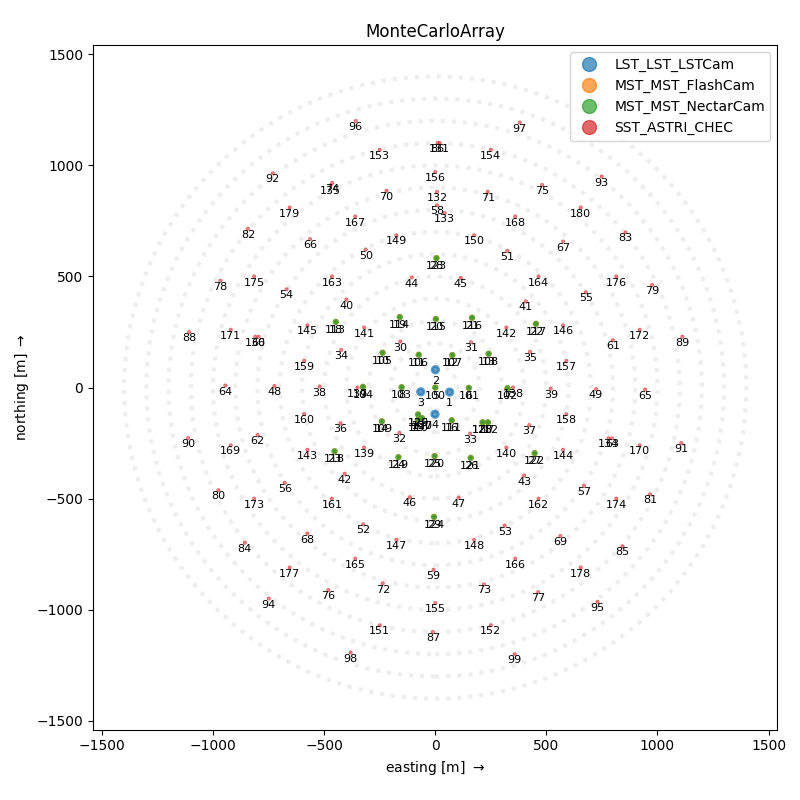
<ctapipe.visualization.mpl_array.ArrayDisplay object at 0x79f091b47340>
111 subarray.to_table()
114 subarray.tel[2]
TelescopeDescription(type='LST', optics_name='LST', camera_name='LSTCam')
117 subarray.tel[2].camera
CameraDescription(name=LSTCam, geometry=LSTCam, readout=LSTCam)
120 subarray.tel[2].optics
OpticsDescription(name=LST, size_type=LST, reflector_shape=PARABOLIC, equivalent_focal_length=28.00 m, effective_focal_length=29.31 m, n_mirrors=1, mirror_area=386.73 m2)
123 tel = subarray.tel[2]
126 tel.camera
CameraDescription(name=LSTCam, geometry=LSTCam, readout=LSTCam)
129 tel.optics
OpticsDescription(name=LST, size_type=LST, reflector_shape=PARABOLIC, equivalent_focal_length=28.00 m, effective_focal_length=29.31 m, n_mirrors=1, mirror_area=386.73 m2)
<Quantity [ 0. , -0.0377967 , -0.04724547, ..., 0.67088033,
-0.45356484, -0.50081024] m>
<Quantity 386.73324585 m2>
142 disp = CameraDisplay(tel.camera.geometry)

145 disp = CameraDisplay(tel.camera.geometry)
146 disp.image = r0tel.waveform[
147 0, :, 10
148 ] # display channel 0, sample 0 (try others like 10)

** aside: ** show demo using a CameraDisplay in interactive mode in ipython rather than notebook
Part 3: Apply some calibration and trace integration#
163 calib = CameraCalibrator(subarray=subarray)
166 for event in EventSource(path, max_events=5):
167 calib(event) # fills in r1, dl0, and dl1
168 print(event.dl1.tel.keys())
dict_keys([9, 14, 104])
dict_keys([26, 27, 29, 47, 53, 59, 69, 73, 121, 122, 124, 148, 162, 166])
dict_keys([82, 92, 175, 179])
dict_keys([17, 26, 27, 29, 43, 47, 53, 57, 69, 112, 121, 122, 124, 125, 128, 140, 144, 148, 162, 166])
dict_keys([3, 4, 8, 9, 14, 15, 23, 24, 25, 29, 32, 36, 42, 46, 52, 56, 103, 104, 109, 110, 118, 119, 120, 126, 127, 129, 130, 137, 139, 143, 161])
171 event.dl1.tel[3]
ctapipe.containers.DL1CameraContainer:
image: Numpy array of camera image, after waveform
extraction.Shape: (n_pixel) if n_channels is 1
or data is gain selectedelse: (n_channels,
n_pixel) with default None
peak_time: Numpy array containing position of the peak of
the pulse as determined by the extractor.Shape:
(n_pixel) if n_channels is 1 or data is gain
selectedelse: (n_channels, n_pixel) with default
None
image_mask: Boolean numpy array where True means the pixel
has passed cleaning. Shape: (n_pixel, ) with
default None as a 1-D array with dtype bool
is_valid: True if image extraction succeeded, False if
failed or in the case of TwoPass methods, that
the first pass only was returned. with default
False
parameters: Image parameters with default None with type
<class
'ctapipe.containers.ImageParametersContainer'>
174 dl1tel = event.dl1.tel[3]
177 dl1tel.image.shape # note this will be gain-selected in next version, so will be just 1D array of 1855
(1855,)
180 dl1tel.peak_time
array([27.381046, 17.746258, 18.80205 , ..., 11.64868 , 31.961287,
29.717525], shape=(1855,), dtype=float32)
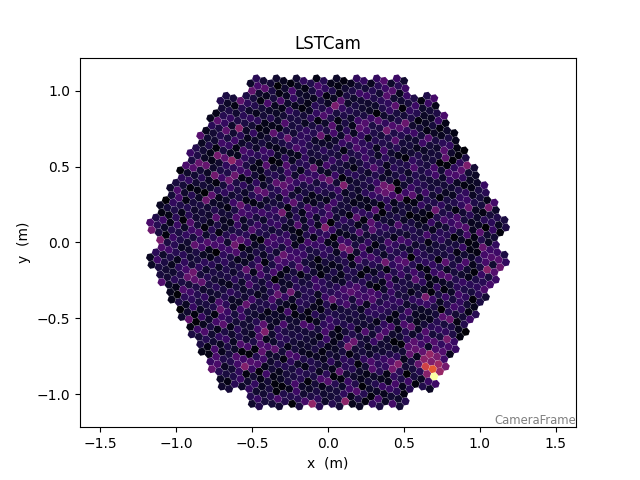
<ctapipe.visualization.mpl_camera.CameraDisplay object at 0x79f097085930>

<ctapipe.visualization.mpl_camera.CameraDisplay object at 0x79f094b58d00>
Now for Hillas Parameters
194 image = dl1tel.image
195 mask = tailcuts_clean(tel.camera.geometry, image, picture_thresh=10, boundary_thresh=5)
196 mask
array([False, False, False, ..., False, False, False], shape=(1855,))

<ctapipe.visualization.mpl_camera.CameraDisplay object at 0x79f091770910>
206 disp = CameraDisplay(tel.camera.geometry, image=cleaned)
207 disp.cmap = plt.cm.coolwarm
208 disp.add_colorbar()
209 plt.xlim(0.5, 1.0)
210 plt.ylim(-1.0, 0.0)

(-1.0, 0.0)
213 params = hillas_parameters(tel.camera.geometry, cleaned)
214 print(params)
{'intensity': np.float64(32.78351974487305),
'kurtosis': np.float64(1.2333006676347782),
'length': <Quantity 0.02219065 m>,
'length_uncertainty': <Quantity 0.00093599 m>,
'phi': <Angle -0.88747705 rad>,
'psi': <Angle -1.56935711 rad>,
'psi_uncertainty': <Angle 2.08329213 rad>,
'r': <Quantity 1.11337613 m>,
'skewness': np.float64(-0.271615381552047),
'transverse_cog_uncertainty': <Quantity 0.00796404 m>,
'width': <Quantity 0.01614423 m>,
'width_uncertainty': <Quantity 0.00226475 m>,
'x': <Quantity 0.70295289 m>,
'y': <Quantity -0.86340237 m>}
217 disp = CameraDisplay(tel.camera.geometry, image=cleaned)
218 disp.cmap = plt.cm.coolwarm
219 disp.add_colorbar()
220 plt.xlim(0.5, 1.0)
221 plt.ylim(-1.0, 0.0)
222 disp.overlay_moments(params, color="white", lw=2)

Ignoring fixed x limits to fulfill fixed data aspect with adjustable data limits.
Part 4: Let’s put it all together:#
loop over events, selecting only telescopes of the same type (e.g. LST:LSTCam)
for each event, apply calibration/trace integration
calculate Hillas parameters
write out all hillas parameters to a file that can be loaded with Pandas
first let’s select only those telescopes with LST:LSTCam
(TelescopeDescription(type='SST', optics_name='ASTRI', camera_name='CHEC'), TelescopeDescription(type='LST', optics_name='LST', camera_name='LSTCam'), TelescopeDescription(type='MST', optics_name='MST', camera_name='NectarCam'), TelescopeDescription(type='MST', optics_name='MST', camera_name='FlashCam'))
245 subarray.get_tel_ids_for_type("LST_LST_LSTCam")
(1, 2, 3, 4)
Now let’s write out program
252 data = utils.get_dataset_path("gamma_prod5.simtel.zst")
253 source = EventSource(data) # remove the max_events limit to get more stats
256 for event in source:
257 calib(event)
258
259 for tel_id, tel_data in event.dl1.tel.items():
260 tel = source.subarray.tel[tel_id]
261 mask = tailcuts_clean(tel.camera.geometry, tel_data.image)
262 if np.count_nonzero(mask) > 0:
263 params = hillas_parameters(tel.camera.geometry[mask], tel_data.image[mask])
267 with HDF5TableWriter(filename="hillas.h5", group_name="dl1", overwrite=True) as writer:
268 source = EventSource(data, allowed_tels=[1, 2, 3, 4], max_events=10)
269 for event in source:
270 calib(event)
271
272 for tel_id, tel_data in event.dl1.tel.items():
273 tel = source.subarray.tel[tel_id]
274 mask = tailcuts_clean(tel.camera.geometry, tel_data.image)
275 params = hillas_parameters(tel.camera.geometry[mask], tel_data.image[mask])
276 writer.write("hillas", params)
We can now load in the file we created and plot it#
283 glob.glob("*.h5")
['hillas.h5']
287 hillas = pd.read_hdf("hillas.h5", key="/dl1/hillas")
288 hillas
291 _ = hillas.hist(figsize=(8, 8))

If you do this yourself, chose a larger file to loop over more events to get better statistics
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 8.326 seconds)

